Abstract: The article presents the process of blowing out PET bottles. PET is processed for various applications due to its very good
physical properties. In the packaging industry, it is used for the production of PET bottles. The concept of blow molding is a process
used to produce hollow objects from thermoplastic. The basic blow molding process has two fundamental phases. The first phase of the
device’s operation consists of heating preforms. The second phase consists in the mechanical extension of the preforms on the axes and
on the extension by means of pre-blowing and then blowing the preforms. The discussion was prepared on the basis of the collected
literature data.
Keywords: INDUSTRIAL COMMODITIES, WASTES, PLASTICS, PET PACKAGING, WASTE MANAGEMENT
1, Introduction
Plastics are an inseparable element of modern human life.
In 2014, 311 million tons of plastics were produced in the
world, which is twenty times more than in 1964. The forecast of plastics production assumes that this number will double by 2036 and will increase fourfold by 2050. Demand for plastics in Europe in 2015 amounted to 49 million tons, of which almost 40% was the raw material used for packaging production. Currently, we distinguish over 1,000 types of plastics, 90% of which come from primary fossil fuels. In Europe, post-production waste plastics are developed by incineration with energy recovery at 39%, they are
deposited in landfills at 31% or derived from
recycling at 30%.
The potential and benefits of plastic products refer to low manufacturing costs, high durability and versatility in use. A large number of positive features also reflect the broadly understood production problems that have a negative impact on the natural environment, climate human life, and health [3].
- Characteristics of PET bottle production process
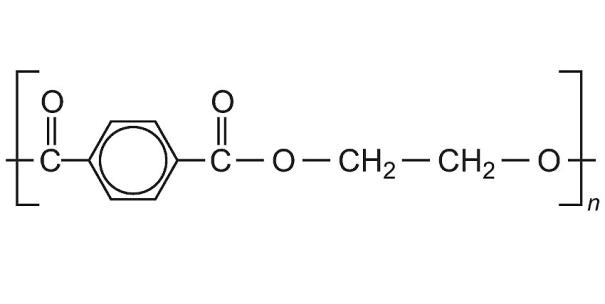
Po Polyethylene terephthalate in short PET is a thermoplastic
polymer from the group of polyesters. Used for the production of synthetic fibers and bottles for non-alcoholic beverages with structural structure
The PET bottle is made using a semi-finished product preform.
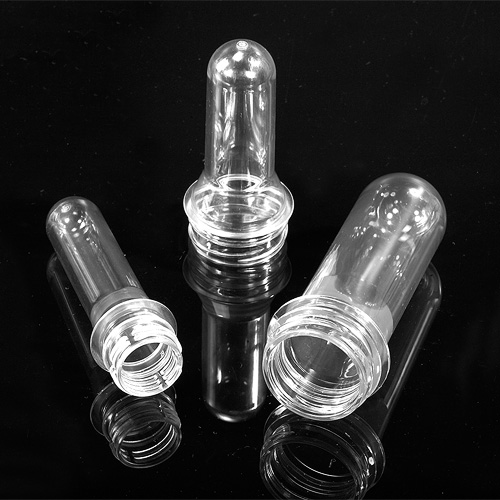
PET preforms are produced in various variants, colors and types. Parameters such as the type of thread, weight, wall thickness and length define the PET preform. It is thanks to them that you can determine what capacity the preform bottle can be blown. A view of an exemplary PET preform is shown in Figure 2 [2,4].
The blasting machine is designed for the production of PET
bottles stretched in two axes. The principle of operation of the
device consists of heating preforms, removing the preforms on the axes mechanically, and pulling them out by pre-blowing and then blowing the preforms.The initial dimensions of the preform depend on the expected stretch ratio to obtain the characteristics of the finished bottle. The degree of stretching is determined by the stretching factor on the two axes, which takes into account the orthotropic development of the preform and, consequently, preferential stretching of the material. Depending on the capacity and use of the bottle, different stretching factors are defined after two axes [4,7].

The stretching process of the PET preform The greater the order in the material structure, the better the mechanical properties of the processed object. In the process of stretching during the production of the bodies, the preforms are reduced by cold blowing with a reduced size in relation to the final shape of the finished product. The stretching takes place along the axes and radially leading to stretching the material along two axes
in parallel, so-called two-dimensional pulling. Figure 2 presents a two-stage process of blowing out a PET bottle
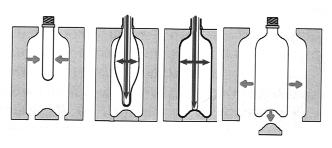
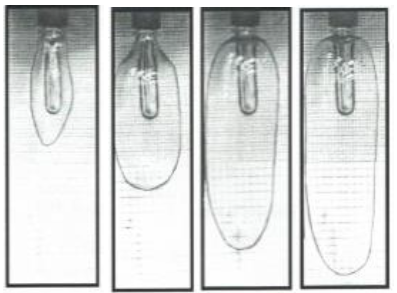
A two-stage stretching process means an internal change in the structure of the material. After completion of the heating process used preform it takes the form of a rubber in the form of liquid rubber. Then, during the stretching step after two axes, the material changes state, where at the end of the blowing process the material takes on a more stable state. Such a change in the state of aggregation is characterized by the “strain hardening” parameter, beyond which the solid-state behavior is obtained. Natural stretch ratio λN. It specifies that during the free blowing of preforms, the drawing coefficient decreases with the increase of temperature and increases with the decrease of the viscosities of the
boundary lines 2 and 3.
Fig. 4. Stresses depending on the stretching factor
Fig. 5. Stress depending on the stretching factor for different
limiting viscosities (temperature 95 ℃)
The choice of intrinsic viscosity depends on the final use of the product. In order to obtain proper mechanical properties in the production of food packaging for carbonated drinks, strong degrees of intrinsic viscosity are assumed. In the case of still drinks in order to obtain the desired degree of mechanical strength, a weak degree of intrinsic viscosity is enough [10,11].
In the initial process of deformation under the influence of
elongation of the tibia and blowing the preform mechanically
weakest parts are deformed first.
The weakest parts are elements having a higher temperature
obtained during the heating of the preform. If the mechanical
properties of the deformed zone exceed the properties of nondeformed
zones, then they deform and develop the bubble.


